Most applications need to keep track of data. Data for preferences, data for cached information, user created data, and much more. There are many different techniques for saving data that your program needs to operate. Collectively, all of these data collection mechanisms can be called “databases.” The following sections describe the various types of database formats.
Plain Unformatted Text Files
While not very robust, text files can be used for such things as temporary saving of a user’s work-in-progress.
Formatted Text Files
These are plain text readable files that come in a variety of options:
- .ini file: Each section has a name in brackets, with individual lines in the format: “Option = value”. Ini files are often used for preference files.
- .csv file: Comma-separated value files have each line with values separated by commas; the first name is similar, but represent column headings
- column aligned files: each line has values where each line’s values start in specific columns, with spaces used as needed
- XML files: these files follow a structured format with opening and closing elements (such as <book> and </book>, with possible data in between the tags. Then, multiple tags can be nested to form somewhat complex structures. XML is an older way to exchange structured text data
- JSON files: more modern applications use JSON files as a way to exchange data. While it is a bit wordy being all text, they are quite readable with little or no explanation. You can easily describe heirarchical data with arrays of numbers or strings, and/or arrays of entire objects enclosed in curly braces.
Relational Databases – SQL
SQL databases. “Structured Query Language” databases are highly organized data repositories that use a special language (originally called SEQUEL) to extract data. This language, as implemented by various SQL product implementations, ranges from relatively simple to quite complex. To illustrate, for all SQL relational databases, the structure of the actual data is basically the same as shown below:
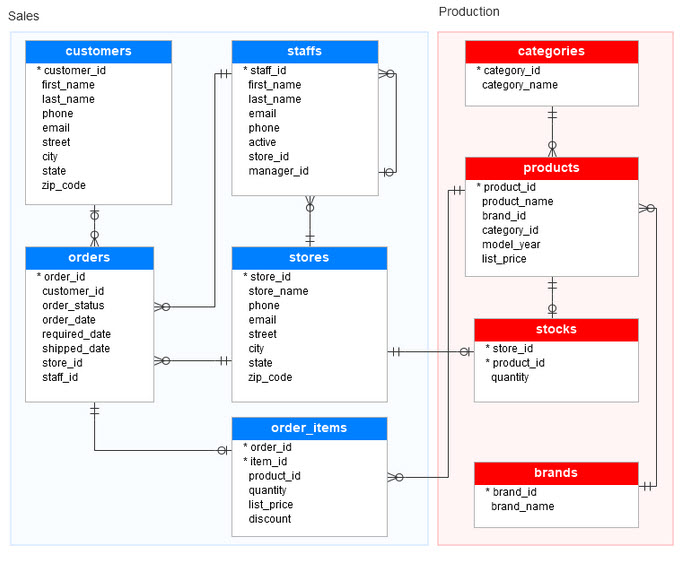
The above diagram shows 2 collections of related tables, each with a set of fields and a primary key (one or more fields). As can be seen, the key field of some tables match a field in another table, therefore making it easy to fetch data from multiple tables based on a common [key] value(s).
What distinguishes the different available SQL relational database products is some of the features as well as other sets of pros and cons. Some of the features available are listed below, broken down by how likely a product is to have the feature:
UNIVERSAL FEATURES
- Table definitions
- Data types: INTEGER, DECIMAL, STRING
- Simple SQL query commands such as SELECT, DELETE, JOIN, CREATE, PRINT, DROP, UPDATE
- Fields declared to be indexes
LESS COMMON FEATURES
- Stored procedures. There are essentially SQL programs saved under a name and allowing input and output parameters
- Functions (System functions like LEN, SUBSTRING, etc.; Additionally, user-defined functions which are procedures returning a single value
- Many more data types, such as BIGINT, FLOAT, REAL, etc.
- Access to the “master table” which has information about tables, functions and procedures available to SQL
The most popular SQL databases for desktop applications are SQLite, MySQL, MongoDB, and Microsoft SQL Server. In this blog I will go into some detail of SQLite and MySQL as can be used in C#.
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases are non-relational databases that need to use alternative means to access specific data records. The most popular NoSQL databases are:
- Document database – These are similar to a text-style database. The typical example is where each document is a JSON file. In particular, you can search the database by a language that allows you to specify the field(s) and their value(s) that could identify one or more documents.
- Key-value database – This simplistic database is simply a collection of key/value pairs. Each record consists of a key name and its value.
- Graph database – Finally, graph databases are the newest type of database often associated with Artificial Intelligence. Rather than go into great detail of this complex structure, suffice it to say that they consist of nodes and edges that are used to traverse various paths to arrive at an “answer.” Neo4j is one of the earliest and most popular graph database products. Graph databases have their own specialized graph database language to query information contained therein.